Hardware Setting & Mode Configuration
Outside the unit, there are four 4-pin DIP switches which are set to select the mode of operation. You will need to set the switch settings to RS-422 mode, or RS-485 mode, as per the requirements of your application.After setting of switches and connecting power supply to the adapter, you then plug the adapter to USB port to start driver installation. The RS-422 & RS-485 Mode Block Configuration Settings are listed as follows.
RS-422 & RS-485 Mode Block Configuration
SW1 (PORT1), SW2 (PORT2), SW3 (PORT3), SW4 (PORT4)
|
|
Operation Mode |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
S4 |
|
RS-422
|
4 wire with
handshaking |
ON |
ON |
OFF |
OFF |
|
RS-485
|
Full Duplex (4 wire) |
ON |
OFF |
OFF |
OFF |
| Half Duplex (2 wire) with Echo |
OFF |
OFF |
OFF |
ON Note |
|
| Half Duplex (2 wire ) without Echo |
OFF |
OFF |
ON |
ON Note |
Note : In the most common situation , a 120 Ohm termination resistor of TxD (S4 is ON ) is required in a RS485 Half Duplex configuration. Otherwise it is rarely used.
Inside the unit, there are four 6x2 (8pin) header blocks which are jumpered to enable Rx, CTS 120 Ohm termination resistors and Rx, Tx 750 Ohm biasing resistor. You will need to open up the case and set the jumper setting for RS-422 mode or RS-485 mode as per the requirements of your application. Settings are listed as follows.
JP5(PORT1), JP6(PORT2), JP7(PORT3), JP8(PORT4)
for Termination and Biasing Option Configuration
|
Jumper |
Function |
|
1-2 |
This
jumper should be populated for pull-up |
|
3-4 |
Pull-down
This
jumper should be populated for pull-down |
|
5-6 |
Rx+/-
Termination of 120 Ohm. This
jumper should always be populated forRS-422 and RS485 Full-Duplex mode. |
|
7-8 |
Pull-up
Rx+ to VCC by 750 Ohm Bias resistor. This
jumper should be populated for pull-up Rx+. |
|
9-10 |
Pull-down
Rx- to GND by 750 Ohm Bias
resistor. This
jumper should be populated for pull-down Rx-. |
|
11-12 |
CTS
Termination of 120 Ohm. This
jumper should always be populated for RS-422 mode. |
Note
: Sometimes, when operating in RS-422 or RS-485, it is necessary to configure
termination
and biasing of the data transmission lines. Generally this must be done
in
the cabling, since this depends on the installation of connections. Before
applying
the
option, check your cable specification for proper impedance matching.
Biasing
of data lines must only occur at a single point anywhere in the cabling. USB‑4COMi-M
and USB‑4COMi‑SI-M provide biasing for ease of installation. Please
be sure to
disable this inside the unit, if your cabling already provides biasing.
Termination
must not be installed in the middle of the cable. It is only permitted at both
ends. Since a computer controlled serial port is almost always at one end of
the cable, termination is enabled by default. Rx‑Termination is inside the box,
because you hardly ever need to change it. Tx‑Termination is used in Half‑Duplex
modes. In this situation data is sent and received
via Tx+/- lines. Therefore Tx‑Termination is done via DIP‑Switch
(see
S4 above).
RS-422/485
Pin-outs & Signal Wiring
|
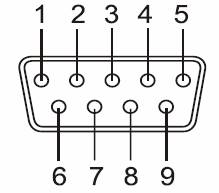
are Setting & Mode Configuration
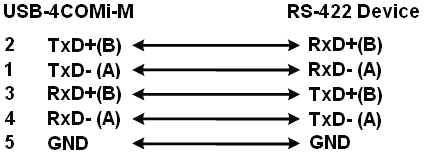
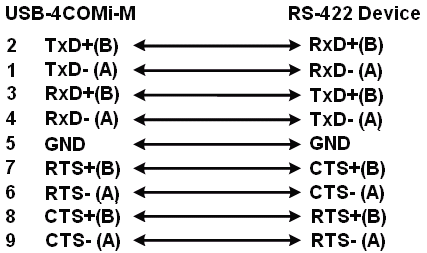
RS-422 Signal Pin-outs of DB-9 Male
|
Pin 1 |
TxD- (A) |
|
Pin 2 |
TxD+(B) |
|
Pin 3 |
RxD+(B) |
|
Pin 4 |
RxD-(A) |
|
Pin 5 |
GND |
|
Pin 6 |
RTS- (A) |
|
Pin 7 |
RTS+(B) |
|
Pin 8 |
CTS+(B) |
|
Pin 9 |
CTS- (A) |